Sustained agricultural production is very much essential in developing countries to battle against the poverty and hunger crisis. Agricultural technology involving GM or genetic modification technology is also essential to properly address the food security problems. The review says that advanced GM technology has grown commercially and has shown improvement to benefit the environment, social, economic and human health aspects. There are still lots of controversies regarding the use of GM technology in agriculture.
Genetically modified crops are so popular among the public due to the various benefits and risks involved in it. The genetically modified crops were produced in large quantities in the previous decade in both developed and developing countries. But, the impact of GM crops on the environment and human health has been a big debate all over the world, though no particular health problem was proved to have existed. In contrast, the benefits of GM crops towards the environment and health have been documented. Rapid industrial growth has introduced the risks of restricted food supply which is a major issue among those that are contradicting the benefits of GM crops.
As the population grows exponentially in developing countries, people suffering from poverty have also increased. The green revolution has brought profits to mostly Asians and Latin Americans than the Africans. About one million people in Asia were benefited by the green revolution because of the rice and wheat that were produced in large quantities in Asia. Asian green revolution was also successful due to irrigation, better-quality crops and chemical contributions. The revolution was conspicuous when poverty reduction is concerned. The advent of green revolution continued for several years and slowly the soil environment started changing and the quality of water bodies also was altered. Gradually, the agricultural harvests reduced. It was understood that the threshold of green revolution has reached and there is a need for novel technologies to replace it.
Genetic modification has evolved a new technology that has proved to be potent enough to enhance the crop produce. This article reviews various studies that focused on the use of genetically modified crops in developing countries.
Genetically modified crops in emerging countries
GM crops were commercialized since 1996. China and United States were known to have marketed GM crops prior to 1996. GM crops did not become popular in Europe, Japan and North America. Since 1996, the commercialization has improved from 1.7 million hectares of the global area of GM crops to 148 million hectares by 2010. The growth was estimated at 8,606 percent. GM crop technology has become a faster crop technology by 2010 and the countries commercially dependent on these crops increased from 6 to 29. India and China were leading GM crop producers in Asia, Brazil and Argentina were leading in Latin America, South Africa in Africa, and the United States and Canada in North America.
| Area | Country Name |
| 3.5 | China |
| 9.4 | India |
| 0.7 | Australia |
| 22.9 | Argentina |
| 25.4 | Brazil |
| 2.2 | South Africa |
| 0.3 | Burkina Faso |
| 66.8 | United States |
| 8.8 | Canada |
Area in Million hectares of land used for GM crop production in 2010
The area of the Bt GM crops that were planted in 2010 constituted 73.3 million hectares of Bt soya bean, 46.8 million hectares of Bt Maize, 21 million hectares of Bt cotton, and 7 million hectares of Bt Canola. The herbicide resistance characteristic of these four Bt GM crops was found in 63 percent of the total area planted while insect resistant characteristic was present in 17 percent of the total area. Out of all the farmers (15.4 million) involved in planting GM crops all over the world in the year 2010, 6.5 million were from China and 6.3 million from India.
Impression of Genetically modified crops
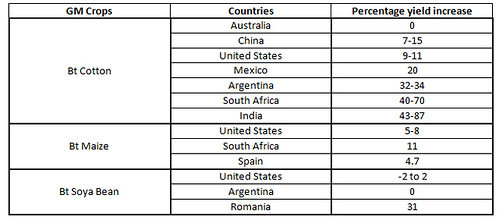
The impact of GM crops on farm level was evaluated by Brookes and Barfoot. The GM technology commercialization was observed to have improved the income of the farmers globally by $ 52 billion from the year 1996. The increase in income of the farmers growing Bt GM crops like Bt cotton, Bt maize, Bt, Soya bean and Bt Canola apart from the other crops was observed as 5.7 percent in the year 2008. The impact of GM crops on production was 79.7 million tonnes of corn production, 8.6 million tonnes of cotton production, 74 million tonnes of soya bean production and 4.8 million tonnes of canola production. Genetically modified crops have shown improvement in the yield, production and gross margin profitability of the various countries. The average increase in profitability on the gross margin created by GM crops were US $ 58 per hectare, $ 66 per hectare, $ 470, $ 295, $ 135, $ 91, and $ 23 in the United States, Australia, China, Mexico, India, South Africa, and Argentina respectively.
GM crops were also found to have shown a positive impact on the environment by reducing the emission of greenhouse gases. The impact of GM crops on human health was also positive as the use of pesticides was reduced.
Reference
Ademola A. Adenle. Global capture of crop biotechnology in developing world over a decade. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (2011) 9, 83-95.
About Author / Additional Info: