Authors: Poonam Kumari, Thaneshwari and Sapna Panwar
Division of Floriculture and Landscaping
ICAR- IARI New Delhi- 110012
Correspondence address: poonamjaswalfls@gmail.com
INTRODUCTION
- Flower crops are attacked by several pests and diseases.
- Several pests act as vectors for various diseases which cause considerable yield loss.
- Chemical control is expensive, time being and health hazardous.
- Genetic resistance is the cheapest and the best method of minimizing such losses.
- Resistant varieties are developed through the use of resistant donor parents available in the gene pool.
- Many crops would have lost their commercial status if resistance to the particular diseases were not available. Initially to obtain resistant varieties knowledge of genetics with respect to pest and disease is essential In pest and disease,
- Oligogenic resistance
- Polygenic resistance
- Cytoplasmic resistance
- The relationship between a plant and plant pathogen is very complex
- The ability of a plant pest or pathogen to cause disease in a plant depends on environmental conditions, the properties of the organism itself and the capacity of the plant to defend itself
- Varieties within a plant species can differ in their ability to defend themselves
- Under different climatic conditions the interaction between the same plant and plant pathogen may have different outbreak
- Plant pathogens are known to develop and form new races or strains that can cause damage to plants that remain unaffected by the original form of the pathogen
Resistant varieties
A variety is known to be resistant, if the pest cannot eat it, or cannot live or multiply on it. Thus, if a plant is resistant against a pest, it will not suffer any damage from that pest.
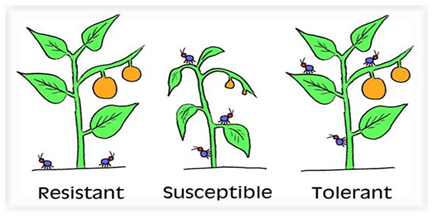
ADVANTAGES OF RESISTANT VARIETIES
- Resistant varieties offer cheapest means of disease control as they do not involve in any recurring expenditure to farmer
- Resistant varieties obviate the use of pesticides, thereby in reducing the crop production, environmental pollution and health hazards
- It safeguards against the inadvertent release of such varieties that are more susceptible than the earlier varieties
- Not affected by environmental conditions
- It can be used in IPM
- It helps in protection of natural enemies (Predators & Parasites)
PESTS AND DISEASES OF FLOWER CROPS AND RESISTANT VARIETIES
ROSE
Major diseases
Black spot: Diplocarpon rosae
Powdery mildew: Sphaerotheca pannosa var. rosae
Botrytis blight: Botrytis cinerea
Crown gal : Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Other diseases: Stem canker, Cercospora leaf spot, Rust etc
Major pests: Aphids, Two-spotted spider mite, Scale insects, Thrips (Florida flower and western flower, chili thrips), Beetles and Leaf-cutter bees
Rose varieties resistant to Blackspot:
Angel Face, Ivory Fashion, Proud Land, Carrousel, Miss All-American Beauty, Queen Elizabeth, Duet Mister Lincoln, Razzel Dazzle, Electron, Montezuma, Rose Parade, Europeana, Pink Peace, Sonia, First Edition, Portrait, Tiffany, First Prize, Pristine, Morden Ruby, Tropicana, Gene Boerner, Prominent, Morden Blush, Morden Snow Beauty, Parkland
Hybrid tea: ‘Pride N Joy’
Floribunda: ‘Sexy Rexy’
Grandiflora: ‘Prima Donna’
Roses Resistant to Blackspot :
Shrub : Care Free Spirit, Pink Knock Out, Rainbow Knock Out, Winter Sunset
Floribunda : Rainbow Sorbet, Julia Child
(Prima W. K. Hutabarat , 2012)
Black Spot & Powdery Mildew resistant roses: Moderately resistant varieties
Hybrid tea: ‘Duet,’ ‘Eiffel Tower,’ ‘Grand Slam,’ ‘Jamaica,’ ‘Matterhorn’
Floribunda: ‘Golden Slipper,’ ‘Saratoga’
Grandiflora: ‘Camelot,’ ‘John S. Armstrong,’ ‘Pink Parfait,’ ‘Queen Elizabeth’
Shrub roses: ‘All That Jazz,’ ‘Carefree Wonder’
Black Spot, Powdery Mildew & Cercospora Leaf Spot resistant varieties
Rugosa roses: ‘Blanc Double de Coubert,’ ‘Fru Dagmar Hastrup’ (‘Frau Dagmar Hartopp’) ‘Rugosa Alba,’ ‘Topaz Jewel’
Alba rose: ‘Alba Semi-Plena’
Cercospora Leaf Spot resistant roses
Jeepers Creeper, Ralph’s Creeper, Royal Bonica, Nearly Wild, Betty Prior, Sevillana, Magic Carpet, Easy Livin’, Cherry Meidiland, Pearl Meidiland, Rosa mutabulis, Rosa wichuraiana, First Light, Bonica, Carefree Wonder, Sea Foam, Pink Grootendorst, Nozomi, Red Cascade, Mystic Meidiland, Hansa, Double Delight
Resistance against mites:
- Grzeszkiewicz and Witaszek (1994) evaluated 26 rose cultivars for cut flower yield and quality and for resistance against T. urticae and reported that Parfait, Lady Rose and Hidalgo cultivars were found most resistant to T. urticae.
- Dhooria (1999) studied the mite damage on 7 rose varieties under polyhouse condition. Maximum mite damage was noticed on variety Prophyta (53%) followed by Sophire (23%), First Red (17%), Mercedes Long (15%) and Vivaldi (13%) and negligible mite damage was observed in varieties ‘Golden Time’ and ‘Pavarroti’.
- Hole and Solunkhe (2005) screened thirty rose cultivars for their relative resistance against two spotted spider mite, T. urticae and reported that the cultivar Rajhans recorded the lowest mite population followed by Apsara and Rose Evening.
- Tinike, Skyline, Confittee, Grand Gala and First Red
(Dhananjaya Kumar K.S, 2007)
- Gahukar (2003) studied the reaction of three rose varieties against thrips under field condition and reported that over 50 per cent infestation was observed in Gladiator; 40-42% infestation in Folklore and 24-25% infestation in Landora during 1996 and 1997.
- Skyline, Confetti, Tinike, Grand Gala, First Red (Dhananjaya Kumar K.S, 2007)
CARNATION
Major diseases
Fusarium wilt, Foot rot, Basal rot, Leaf spot and Botrytis blight
Major pests
Thrips, Mite and Bud caterpillar
Resistant varieties
- Onozaki et al., (1998) developed a line 91BO4-2 by crossing spray type cv. Super Gold with Dianthus capitatus (wild). This line was highly resistant to bacterial wilt.
- Ben et al., (1997) reported that cv. Arbel and Scarlette had novel resistance against Fusarium wilt.
- Cultivars William Sim and Vermillion Protruding were less susceptible to stem rot amongest the twelve cultivar tested by Guba et al., 1997.
- cvs. Krassina, Regina, Fea, Naslada, Line L-169 and Line L-230 (Slavov et al., 2006)
- Arbel and Scarlette (Y. Ben-Yephet et al., 1997) CHRYSANTHEMUM Major diseases Fusarium wilt, Rust, Root rot, Powdery mildew, Leaf spot & Flower blight. Major pests Aphids, Bud caterpillar and Thrips Rust resistant varieties: ‘Achievement,’ ‘Copper Bowl,’ ‘Escapade,’ ‘Helen Castle,’ ‘Mandalay,’ ‘Matador, ‘Miss Atlanta,’ ‘Orange Bowl,’ ‘Powder Puff.’ GERBERA Major diseases Foot rot, Fusarium wilt, Blight or Grey mold, Powdery mildew and Phyllody Major pests Thrips and Bud borer Table 1. Gerbera varieties resistant to foot rot ( Phytophthora cryptogea)
| Hybrid | Florets colour | Disc colour | Resistance of (Phytophthora cryptogea) | Vase life-water days |
| H 229/3 | cream with pink line | green | Highly resistant | 15.2 |
| H 134/8 | yellow | dark brown | Resistant | 13.8 |
| H 147/5 | light pink with pink line | dark brown | Resistant | 12.7 |
Table 2. Reaction of gerbera varieties against powdery mildew
| Varieties | Disease reaction | Number of flowers /m2/year | Number of sucker /plant / year |
| Figaro | Resistant | 143.00 | 3.80 |
| Marinila | Resistant | 106.60 | 4.00 |
| Palmira | Resistant | 190.00 | 5.40 |
Sirtaki, Rondena, Fame and Bianca (Krips et al.,2001)
GLADIOLUS
Major diseases
Fusarium wilt, CMV (Cucumber mosaic virus)
Major pests
Thrips and Spike caterpillar
Wilt resistant gladiolus varieties
- Novalux and White Prosperity resistant cultivars (Dallavalle et al.,2002)
- Cultivars Albana, Apricot Glow, Souvenir, Hoppman’s Glory, Sylvia, Dhiraj, White Friendship and White Prosperity are reported to be resistant while Australia Four and Mansore are tolerant to wilt disease (Mc Cullough, 1944; Georgiaand Peikova, 1976; Sezginet al.,1983, Chandra et al., 1985 ; Bajaj et al., 1989).
- In gladiolus, out of 11 cv. Tested against the disease cvs ‘IARI Set 1’, ‘Psittacinus Hylo and Sueliton were found resistant (Sharma and Bhattacharjee, 2002). Table 3.Wilt resistant gladiolus varieties
| Cultivars | Parent | Resistance |
| Arka Amar | Watermelon Pink X Aarti | Resistant |
| Arka Kesar | Vink’s Glory X Sagar | Moderate resistant |
| Darshan | Watermelon Pink X Shirley | Moderate resistant |
| Dhiraj | Beauty spot X Psittacinus hybrid | Resistant |
| Kum Kum | Watermelon Pink X Lady John | Moderate resistant |
Major diseases
Collar rot & root rot, Fusarium wilt, Rust, Grey mold and Aster yellows (Virus)
Major pests
Stem borer, Mites and Nematodes
Fusarium wilt resistant china aster varieties
“Heart of France”, “Crego” , “Ostrich”, “Feather”, “ Stardust”, “American Branching”, “Roment”, “Powderpuff” and “Lapplator” (Jones and Riker)
“Srdce Francie” and “Bukett Bila” (Kratka and Duskova, 1991)
Resistant: Matsumoto, Einf. Madeleine and Americka Kraska series
Moderately resistant: Chryzantemokvěte and Standy series, Matsumoto Pink, Princes Armida and Jitka (Nečas and Kobza 2008).
Nematode (Meloidogyne incognita race 1) resistant varieties:
Highly resistant: IIHR-2
Resistant : Shashank, AST-5, IIHR-17 and IIHR-21
Moderately resistant: Poornima (Nagesh et al.,1995)
Rust resistant china aster varieties:
New England Aster (A. nova-angliae): ‘Crimson Beauty,’ ‘Fanny’s,’ ‘Harrington’s Pink,’ ‘Honeysong Pink,’ ‘Purple Dome,’ ‘Wedding Lace.’
Wood Aster (A. dumosus): ‘Wood’s Blue.’
TUBEROSE
Major diseases
Basal rot
Major pests: Aphids, Thrips ,Bud borer and Root knot nematode
Resistant tuberose varieties
Nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) resistant varieties:
Shringar : resistant
Suvasini : moderately resistant
CROSSANDRA
Major diseases
Wilt : Fusarium solani
Stem rot : Rhizoctonia solani
Leaf blight : Colletotrichum crossandrae
Alternaria leaf spot : Alternaria amaranthi var. crossandrae
Major pests: Root knot nematode and Aphids
MARIGOLD
Major diseases
Leaf spot
Wilt and stem rot
Bacterial blight
Major pests: Root knot nematode, Aphids
Alternaria leaf spot resistant marigold varieties:
‘Golden Guardian’ and ‘Doubloon.’
References:
Kumar, S., Tomar, K. S., and Shakywar, R.C., 2012, Response of gerbera varieties against powdery mildew disease under polyhouse condition. HortFlora Research Spectrum, 1(3): 286-288.
Cantor Maria and Lenuta Chis, 2006, breeding of gerbera hybrida at the fruit research station Cluj. Buletin USAMV, ISSN 1454-2382.
Grzeszkiewicz, W.H. and Witaszek, W., 1994, Evaluating the suitability of 26 rose cultivars grown for cut flowers in heated plastic tunnel. Zeszyty Noukowe, Instytutu Sadownictwa i kwiaciarstwa w skienriewicach,, 1 : 85-94.
Dhooria, M. S., 1999, Two spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae a serious pest of roses in polyhouses and its control. J. Acarol., 14 (1&2) : 84-87.
Gahukar, R. T., 2003, Factors influencing thrips abundance and distribution on rose flowers in central India. J. Entomol. Res., 27 (4) : 271-279.
Hole, U. B. and Salunkhe, G. N., 2005, Studies on the relative resistance of rose cultivars to two spotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae Koch.). J. Maharashtra Agril. Univ. 30 (3) : 316-317.
Dhananjaya Kumar K.S, 2007, Incidence and management of mites and thrips of rose under naturally ventilated polyhouse condition. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Agr icultural Sciences, Dharwad.
Krips OE, Willems PE, Gols R, Posthumus MA, Gort G, Dicke M.,2001, Comparison of cultivars of ornamental crop Gerbera jamesonii on production of spider mite-induced volatiles, and their attractiveness to the predator Phytoseiulus persimilis. J Chem Ecol. 27(7):1355-72.
Prima W. K. Hutabarat, 2012, Morris Arboretum Nursery Trial: A Study of Rose Care Treatment.
Onozaki, T., Ikeda, H., Yamaguchi, T., 1998. Effect of calcium nitrate addition to a-aminoisobutyric acid (AIB) on the prolongation of the vase life of cut carnation fowers. J. Jpn. Soc. Hort. Sci. 67, 198- 203.
Ben-Yephet, Y., M. Reuven, and D. Shtienberg. 1997. Complete resistance by carnation cultivars to Fusarium wilt induced by Fusarium oxysporum f sp. dianthi race 2. Plant Dis. 81:777â€"780
About Author / Additional Info:
Ph.D Scholar at Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi