Authors: Ravi kumawat, Madhu Choudhary, Kana Ram Kumawat
- Encapsulation of tissue culture derived somatic embryos, shoot buds, cell aggregates or any other tissue that can form a plant on sowing as seed in field and can be stored is known as synthetic seed.
- The concept of synthetic seed was first conceived by Murashige (1978) and first synthetic seed was prepared by Kitto and Janaick (1982).
- Synthetic seed is an effective and efficient alternate method of seed production and availability that has developed new vista in agriculture.
Material and method:
Equipments â€" autoclave, incubator, analytical balance, pH meter, hot plate
Chemicals- distilled water, MS medium, Sodium alginate, Calcium nitrate,
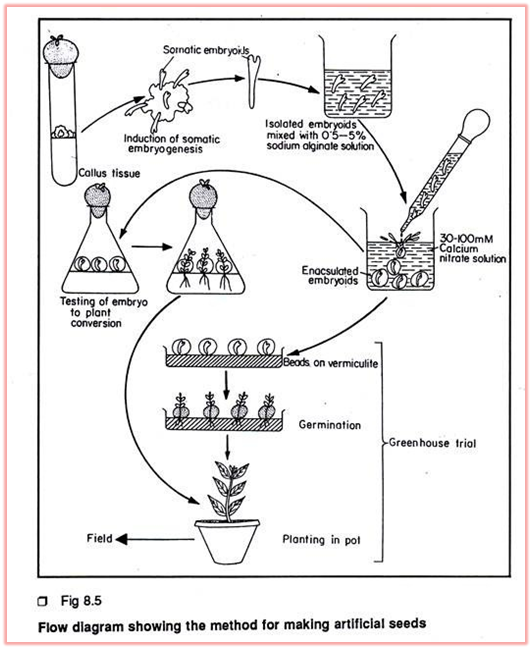
Procedure:
A. Preparation of nutrient medium: Required quantity of MS medium is dissolved in sterilized water and supplement with growth regulators and 6-8 g agar/liter of the medium.
B. Isolation of explants: Healthy organ is selected and sterilized with 2 % sodium hypochloride solution rinsed with distilled water.
C. Inoculation of explants: 1 mm thickness slices are cut from the desired tissues and transferred in test tube containing MS medium. The somatic cells developed into differentiated embryos, and each embryo is capable of developing into a plantlet.
10-20 weeks structures are isolated.
E. Encapsulation of somatic embryos: Synthetic seed is encapsulated to simulate the seed coat and endosperm. The alginate hydrogel was found most suitable for Encapsulation.
F. Storage of synthetic seeds: The growth of somatic embryos occurs without any lag phase. These seeds are stored in dark for 10-20 weeks at 250 C at 40-50 % relative humidity.
G. Germination and seedling establishment: The somatic embryos turns green with initiation of root and shoot are considered as seedling.
Advantages of synthetic seed
- It assure availability of planting material
- Fast multiplication
- It assures genetic purity of seed
- Low cost, high volume propagation system in comparison to true seeds and transplants.
- An alternate viable technology for vegetative propagated crops.
- The plant slow or difficult in propagation may be multiplied vary fast
- Easy transportation of seed in comparison to the crops multiplied vegetatively.
- Pathogens transmitted through vegetative parts are checked.
- It improves the storability in comparison to vegetatively parts as seed
- Synthetic seed is an alternate to maintain hybrid vigour without production of hybrid seed production.
- We have to wait upto end of reproductive phase for obtaining true seeds. But artificial seeds are available within at least one month.
- The production of true seed is season bound at particular seasons of a year. But production of artificial seed is not time or seasonal bound.
- Life cycle of plant could be shortened in case of plant where dormancy of seed is prolonged.
- Artificial seeds will be applicable for large scale monoculture as well as mixed genotype plantation.
- It gives the protection of meiotically unstable, elite genotype.
- Artificial seed coating also has the potential to hold and deliver beneficial adjuvant such as growth promoting rhizobacteria, plant nutrients and growth control agents, and pesticides for precase placement.
- Artificial seeds help to study the role of endosperm and seed coat formation
- We have to wait upto end of reproductive phase for obtaining true seeds. But artificial seeds are available within at least one month.
- The production of true seed is season bound at particular seasons of a year. But production of artificial seed is not time or seasonal bound.
- Life cycle of plant could be shortened in case of plant where dormancy of seed is prolonged.
- Artificial seeds will be applicable for large scale monoculture as well as mixed genotype plantation.
- It gives the protection of meiotically unstable, elite genotype.
- Artificial seed coating also has the potential to hold and deliver beneficial adjuvant such as growth promoting rhizobacteria, plant nutrients and growth control agents, and pesticides for precase placement.
Artificial seeds help to study the role of endosperm and seed coat formation.
About Author / Additional Info:
I am pursuing Ph. D from MPUAT, Udaipur