Authors: Kuldeep Srivastava, Amrendra Kumar, R.K. Patel and J P Verma
ICAR-NRC on Litchi, Muzafarpur, Bihar (842002)
Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn) is an important subtropical evergreen fruit crop belongs to family Sapindaceae. It has high nutritive value and refreshing taste. Litchi is consumed as fresh fruit, pulp and various processed products like squash, RTS, beverages, etc. Litchi appears to be native of the area, near Southern province of China and northern Vietnam from where it was introduced into India during the 18th century in the North East region (Tripura) and over the period of time to eastern states and percolated in the northern states. It is now an important commercial fruit crop in India due to its export potentiality. Cultivation of litchi is widely spread in eastern India which provides livelihood opportunities to millions of people in the region. It is commercially grown in Bihar, Uttarakhand, West Bengal and Jharkhand. Due to its high economic returns and ever increasing demand in the domestic markets, the crop is also gaining momentum in Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Assam, Tripura, and Orissa. Considering the importance of this fruit crop in the region, efforts are made to provide technological support through research and promoting production, post-harvest management and marketing. The litchi growers are facing serious problem of many insects pests like fruit borer, litchi mite, shoot borer, bark borer, leaf minor, leaf webber, etc. and as such the production is reduced drastically with marketability. Litchi mite is the threat to litchi growers as both nymphs and adults damage the leaves, inflorescence and young developing fruits through sucking of sap form newly emerged shoots. Due to continuous sucking of sap by the nymphs and adults, leaf tissues become aggravated and formed erinium. The maximum incidence of the mite was seen during October - November month especially in unprunned orchard. Therefore, keeping in view the importance of litchi mite a field trial was conducted to evaluate the different IPM modules against litchi mite. By adopting integrated management schedule this noxious pest can be managed. A brief . A brief description of pest and its nature of damage along with integrated management schedule developed at ICAR-NRC on Litchi have been given.
Description
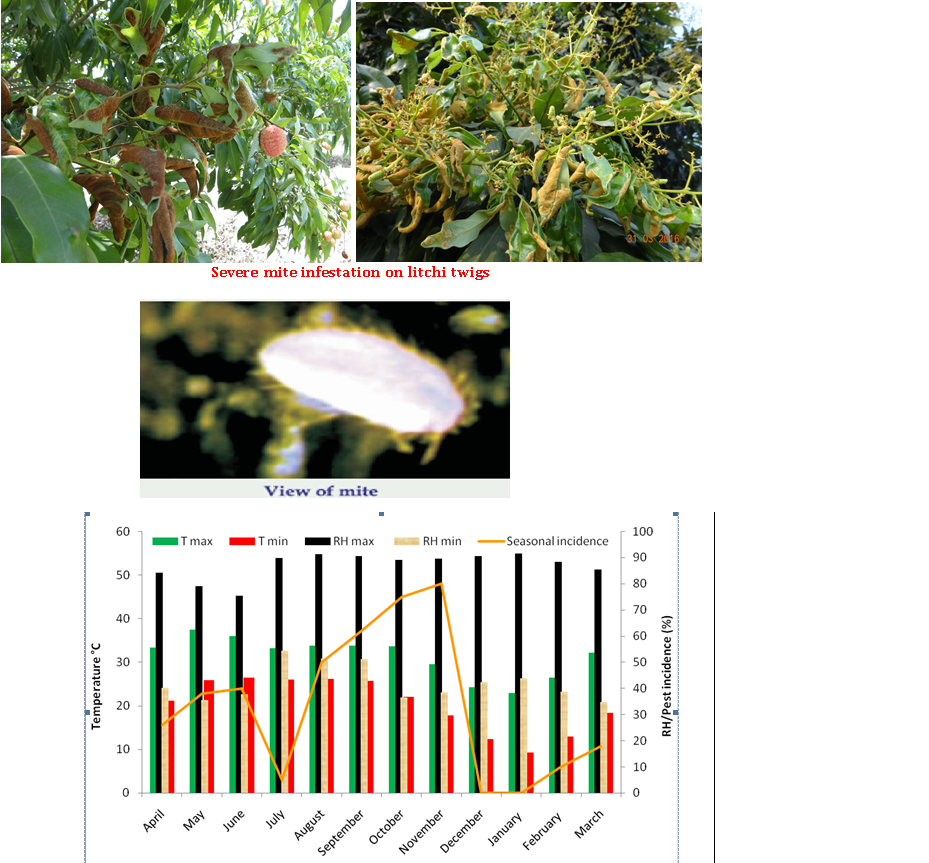
Litchi mite is a tiny creature which is not visible through necked eye. Both nymphs and adults of mite damage the leaves, inflorescence and young developing fruits through sucking the sap form newly emerged leaf lamina, shoots and developing inflorescence and fruits. Due to continuous sucking of sap, leaf tissues become aggravated and form erineum. The symptom occurs as velvety growth on the lower side of leaf surface which enlarge and turn to chocolate colour with deep lesion resulting in reduced or no photosynthesis from affected area. In severe cases particularly in unmanaged orchards, the infestation level become very high and spread of the infestation takes place from the neighboring plants and orchards. In such orchard, very poor flowering and fruiting takes place and growers suffers from huge economical losses. The maximum incidence of the mite is noticed during the July-October and February-March especially in un-pruned and poorly managed orchard.
The population of mite changes with change in weather parameter and maximum population of mite seen during post rainy season in north Indian condition. So for effective management of litchi mite the October- November and March is the critical time.
Management Schedule
• Pruning and removal of infested twigs/ shoots just after harvesting of the fruit before new emergence of new flush.
• Two spray of chlorfenapyr 10 EC (3ml/l) or propargite 57 EC (3ml/l) at 15 days interval during July.
• Pruning of newly infested twigs during October and spray with chlorfenapyr 10 EC (3ml/l) or propargite 57 EC (3ml/l).
• In case the pest is seen, need based spray of above acaricides after panicle initiation and before flowering may be given to control the mites.
Precaution/ Alertness
• Field sanitation and pruning of infested shoots, leaves and plant parts.
• Pest load may be kept under control during the growth phases of litchi plants.
• Pest monitoring and timely control measures must be followed.
Safety Measures
• Pruning of trees after harvest, field sanitation and removal of young fallen fruits for reducing pest population
• Spraying of acaricides should be done at outer as well as inner canopy from all direction of the tree with the help of power sprayer having hollow cone nozzles
• Spraying to be imposed only during clean weather, to avoid repeat spray in case of rain event.
• Use sticker 0.4ml/l for better results and improved effectiveness during rainy season.
• Community based approach is required for effective management of litchi mite.
References:
Kumar, A. Srivastava, K., Patel, R. K. and Nath, V. 2014. Management of litchi fruit borer and litchi mite using bio-rational approaches under subtropics of Bihar. The Ecoscan, Special issue, Vol. VI: 285-289
About Author / Additional Info:
I am working as Senior Scientist (Entomology). Working on integrated management of litchi pests.