Authors: Rakesh Kumar Parshant Bakshi,Vijay Kumar, Sushil Sharma, Bhart Bushan and Reen
INTRODUCTION
Strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch) is one of important fruit crops in temperate region. However, it can also be grown in the tropical and subtropical climate. Strawberries are among the easiest fruits to rise in kitchen garden, decorative pots, hanging basket and are grown in flat or raised beds and protected cultivation. Strawberries are an excellent specialty crop for local as well as international markets. The area under cultivation this crop in subtropical and tropical region is very low and thus the fruit price remains very high (350- 500 kg). That is the reason poor community cannot eat this fruit because of their higher cost. As strawberry fruit is a good source of vitamin C (30- 100mg/100g of fruit) as well as foliate and photochemical compound such as the elligic acid. Consuming strawberries can reduce the risk of developing cancer by 50% due to higher levels of vitamin C. Beside vitamins sugars are the main soluble components in ripe strawberry fruit, with glucose, fructose, and sucrose accounting for almost 99% of total sugar content. Glucose and fructose are predominant over sucrose, and the total sugar content can change during the growing period. Like sugars, organic acids are important for flavor, and the sugar/acid ratio is calculated to determine the optimum time for strawberry harvesting, ecause it is considered an index of quality. It is the only fruit crop that starts paying back within five months from fruits and nine months from runner after transplanting of runners. It easily propagates itself by the vegetative method of runner production in hilly region. However, it is difficult for the plant to propagate in plains because the mother plant cannot withstand severe hot and drought condition in June and July months and the plant usually dies above 400C. In plain areas runner production is possible only under 75% shade nut and requires proper management of field to safeguard the daughter plants of strawberry during summer. It is main reasons the runner’s production is tropical and subtropical areas are very low. In plain’s strawberry growers can not afford due to higher prices per runner and also the farmers seldom go for its cultivation in plain as they have pay to purchase planting material every year from temperate fruit growers. Whereas in hilly areas every plant produces more than 7 to 8 runner due to their low temperature during regeneration period.
NATURE OF STRAWBERRY PLANT
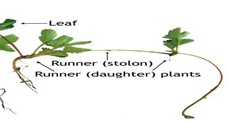
Cultivated strawberry is a perennial crop in temperate region and that produces leaves, flowers stolons (runner) roots in patterns determined by its genetic makeup. Usually, strawberry has two types of roots, the large primary ones and small secondary lateral roots
GROWTH OF CROWN
Cultivate strawberry plant has a short thickened stem (called a “crown”) which has a development point at the upper end and which forms roots at its base. New leaves appear with a bud in the axil of each leaf and flower clusters emerge from “fleshy buds” in the crown in the early spring. From a cultural viewpoint, it is desirable in our region to have the formation of 1-2 “side stems” called crown
SELECTION OF CULTIVARS
Selection of cultivars are most important component to remunerative this crop. Each cultivar is different in fruit size, colour, tests, aroma, firmness and their regeneration
Listing of some important cultivars
Chandler: It is very popular and highly demanding present -day cultivar of Jammu plains region. However, it is commercially grown in northern plain regions of India. Chandler cultivar was developed in California by crossing Douglas and Cal72.361-105. It is high-yielding and resistant to physical damage from heavy rains. Its fruits have exceptionally high quality, large fruit size (15-25g) outstanding colour, large fruit size and good regeneration capacity in hilly areas.
Senga Sengana : It is a cross between Markee and Sieger and introduced in 1952 in Europe and in India in 1980. Its fruits have very attractive red colour and have good regeneration capacity in hilly zone
Sweet Charlie: It is suitable for cultivation in plain as well as hills areas. It has been named in honour of the late Charles M. (Charlie) Howard, plant pathologist, at the university of florida, gulf coast research and education centre. It is resistant from anthracnose, fruit rot and its plants are smaller size, good appearance, very tests and good regeneration capacity in hilly region
Gorella: It is cross between Jespa and US 3763 and very popular cultivar in plain region. Its plants are moderate in vegetative growth with course. The fruits are large, conical, and juicy with good flovour. Its plants produces healthy runner in temperate region
Fern: It is introduced in (USA) and Its fruits are very suitable for processing and pulp is firm with excellent flavor. Its plants are vigour and have good capacity of runner production
Belrubi: It is a cross between Pocahonatas and Redcoat. Its fruits having red pulp and are of good quality. It is suitable in subtropical plains region and has good capacity of runner production in hilly region
Egla: It is early ripens and having orange red pulp cultivar. Its plants are produces runner in hilly areas
SELECT ION OF SITE
Selected a planting site is extremely important for strawberry runners production and prevent runner diseases
- Selected site should be proper drainage of rain water and proper light distribution
- Soil should be rich from organic matters
- Avoid low, poorly drainage and wet areas for runner production
- Avoid water logging soil may generate soil born diereses
- Good water drainage both surface and internal drainage is extremely important for control of leather root and red stele both of these diseases are harmful of runner production
- Availability of irrigation facility
- Labour availability for culture practices
SOIL, IRRIGATION AND CLIMATE
Soil
Strawberry can be grown on a variety of soils. For good growth, the runner needs deep, fertile, moist but well drained soil. Heavy soils subject to water logging are completely un suitable They are not particularly sensitive to soil reaction pH. However sandy loam soil with a pH 5.8- 6.5 is suitable for its cultivation and runner production
Irrigation
Irrigation is very necessary during summer’s months to conserve moisture in the soil , sustain plant growth and to encourages increase new daughter plants. As in sub tropical areas when temperature reach above 40 C at that condition strawberry plants are could not serve and they die themselves. So that, irrigation is necessary particularly new daughter plants to reduce water stress and allow rapid growth of roots
Climate
Strawberry can be grown successfully in tropical and sub-tropical areas, where mean maximum temperate 250 to 400 C in summer and minimum temperate of 20 to 100 C in winter. An annual rainfall of 100 to 125 cm is considered adequate.
ORDERING PLANTS MATERIAL
Before purchasing of runners grower must be known that the name of the cultivar, adaptability of those area and have minimum 10-15 numbers of primary roots that are not less than 10cm (4in) in length when measured from the base of the crown. However, cultivars should not be mixed with each other during transplanting time
FIELD PREPARATION AND PLANTING
Preparation of strawberry field
Select the site least six months before transplanting strawberry runners. Land must be prepared well before transplant the strawberry runners. Strawberry is shallow rooted plant Therefore, deep ploughing is not necessary for normal soil. However 2 or 3 ploughing are necessary to prevent perennial and annual weeds.
Advantages of Raised Bed
Strawberries can be cultivated on raised beds which have the following advantages over conventional growing:
(1) They reduce the risk of water logging and soil-borne diseases.
(2) They increase the available rooting depth on shallow soils.
(3) They warm up quickly and so produce early crops.
These advantages in turn lead to higher yields.
PLANTING
The ideal time of planting in hilly is during March- April months and October- November in plains areas. Beds of standard size (15m x2 m) are prepared. Plant to plant distance 60cm and row to row 60cm distance requires to development of healthy runners
TRANSPLANTING
Strawberry runners have shallow roots. Therefore uprooting runners are susceptible to fungus diseases. Therefore runners roots should be treated with 2 gm of bavsitin in one liter water solution before transplanting in the field and treated planting material’s should be done at morning and evening time hours
MANURING AND FERTLIZERS
It is very important to provide adequate organic and inorganic fertilizers for proper growth, development and to obtain healthy runners production. Sufficient amount of FYM 80-85 tonnes/ ha is recommended pre planting dose during land preparation. Meanwhile inorganic fertilizers have been recommended for profitable production of strawberry. 150kgN, 75kg P 205 and 50kg KO2/ha for best to produce the highest yield, fruit weight and runners production
PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
Use of plant growth regulators of strawberry are important for increasing on flowering, fruit setting, fruit development, improve the fruits quality and runner production of strawberry. Among different growth regulators, GA 3 @ 75ppm and 100ppm have been found the best treatments for increase runner production and yield.. However, NAA, Tricontanol and BAP (Benzylaminopurine) can also used to increase the runners production in hilly regions
HARVEST
Strawberry harvest begins in March in subtropical and May in temperate region. Fruit pick every other day or three times a week. Pick the fruit with about 1/4 of the stem attached. The best time to pick is in early morning when berries are still cool. Not all berries ripen at the same time; pick only those that are fully red.
SOME IMPORTANT CULTURAL PRACTICES
Cleanliness
As completed harvesting, mother plants maker rapid growth and development of new runner. Hence, all beds immediately cleaned from unwanted plants
Deblossoming
Strawberry flower buds begin to emerge from the months of February to March are main blossoming phase starts. April month when all plant shown full blossom at that time remove all flowers from the plant in transplanting year to allow growth, to produce runner and leaf canopy for next year. The best method is to pinch the flower stem by hand. Most of the blossom can be removed in three operations two week apart.
Remove Dead leaves
June- July months are usually the best time of schedule leaf sanitation where winter are more severe, the desiccating effect of hot wind will cause many dead leave that need to be removed for improve the runner health and produce more number of leaves.
Uprooting of established runner plant
Before uprooting the runner plant, the field should be well moisture or irrigated and should have acquired sufficient growth and roots. Runners are separated from the mother- plant with the help of scattered or small knife. The right time of uprooting is last week of October to supply the strawberry growers of plain area. Uprooted plants are carefully packed with soil or moist peat around the roots. It will prevent drying of roots and keep them in fresh condition
MANAGEMENT OF WEEDS
Chenopodium album, Doob grass, Portulaca oleracea, Amaranthus retroflexus, Trifolium, and Cyperus rotundus are common weeds occurrence in strawberry field, which are very harmful for runner production and spared runner disease. As Strawberry plant is shallow root system and is poor competitor against weeds for sunlight, uptake soil nutrients. However some weed spices are alternate hosts for pathogen and insects and pests.
CONTROLS
Hand weeding
After harvesting, 4-5 Hand hoeing operation is requires three weeks apart. Hoeing operation should be carried out fortnightly before produce of runner trains. These ensure maintain soil moisture conservation and soil aeration. Moreover new daughter plants can be utilization of proper sunlight and soil nutrients from soil. Proper weed management in field to increase number of runner train /number of runner per train
Herbicides
Herbicides offered the greatest single potential to control strawberry weeds, because hand weeding is no longer practical to control weeds in strawberry field. Paraquat and Diaquat 0.5 to 0.8 kg can be use one or two days before planting. Simazine or 0.2 to 0.3 kg and Lenacil 0.8kg can be used for runner bed. If dry, irrigate before application
DISEASES
Red core ( Phytophthora fragariae ), Verticillium wilt (Verticillium albo-atrum; V.dahlia),Powdery mildew (Sphaerotheca macularis),Anthracnose (Colletotrichum fragariae),Alternaria spot or Black spot (Alternaria alternate f .sp. fragariae), Fusarium wilt (Fusarium oxysporium Sp. Fragariae) and Grey mould (Botrytis Cinerea) are common diseases are found on strawberry plant. Among the diseases, Red core ( Phytophthora fragariae) and Verticillium wilt are more serious diseases have been observed in strawberry runner’s field
CONTROL
(a) Proper weed management
(b) Soil drenching with disinfectant Ridomil 2 gm or Orychloride (0.1%) in one liter water to the reduced red core disease.
(c) Use formalin 5000 liter in 25000 liter water/ha to control of verticullium wilt infection.
References
1. www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~mcclean/plsc431/students98/fleck.htm
2. Human Gene Therapy: Current Opportunities and Future Trends - Page 176 - By G. M. Rubanyi
About Author / Additional Info:
I AM WORKING IN SKUAST â€" JAMMU AS A SCIENTIST